Mr. Adam Durrant is an orthopaedic surgeon who specialises in the treatment of conditions resulting from injury, trauma or degeneration, to the hand, wrist, elbow and shoulder. He has extensive knowledge of the treatment options available and is practicing the latest surgical procedures in his field. Each unique condition that he is presented with is diagnosed precisely and accurately. He offers both arthroscopic and open surgery treatment techniques. Where surgery is not required non surgical options are considered. Rehabilitation activities and follow-up procedures are also offered for every hand, wrist, elbow and shoulder condition he diagnoses.

Injuries
An injury is considered to be damage to any part of our body. Injuries can be classified into a variety of groups. An injury may be described by its cause such as a traumatic injury, an injury caused by disease or illness, or a degenerative injury. It may be classified by its location, such as a brain injury, a spinal injury, or a soft tissue injury. It may also be classified by its activity as with an athletic injury or an occupational injury. Treatment of injuries can vary significantly. The correct course of treatment can depend on the type of injury sustained, the severity of the injury, its location, and the age and health status of the injured person. Whether a medical treatment, surgical treatment, or physical therapy treatment option is proposed, a qualified medical practitioner will advise you of the most appropriate course of action for any injury sustained.
Athletic and
Sporting Injuries
Athletic, or sports injuries, can potentially occur in any sport that is played. Whether it is a contact or non-contact sport, team sport or individual sport, the risk of injury is always present. Naturally there are some sports in which more serious injuries tend to be sustained, such as boxing, car racing, and rugby. And some sports experience more types of injuries than others. For example motorbike and car racers tend to sustain spinal and head injuries, whereas rugby players experience more shoulder, knee, and leg injuries. Athletic injuries can be caused by constant strain and stress on particular parts of the body, such as tennis elbow or runner’s knee, and these injuries usually affect the joints of the body. Contact injuries, either contact with other players, with sporting equipment, or with the ground, usually cause more broken bones or torn tendons and ligaments.
The different sorts of athletic injuries include ligament and tendon sprains, soft tissue bruising and contusions, muscle strains and tears, joint dislocations, and broken bones. The most common symptoms of athletic injuries include swelling, pain, loss of movement, and redness. Immediate treatment of contact athletic injuries usually consist of rest, ice on the injury, compression of the injury, and elevation of the injury (R.I.C.E.). If the injury sustained is serious enough, then anti-inflammatory drugs may be necessary in order to reduce swelling and enable the body to heal properly. Pain relief may also be required if the injury is causing immobility and too much pain. For serious contact injuries such as broken bones or torn ligaments and tendons, surgery may be necessary to help fuse bones together correctly or reattach ligaments and tendons.
So what are some of the ways to prevent athletic injuries? It is important to thoroughly warm up before exercising and warm down after in order to keep muscles, ligaments, and tendons supple and flexible and blood flowing to all parts of the body. Correct use of sporting equipment and safety equipment is vital to prevent potential athletic injuries. Understand the correct body mechanics for your particular sport. Being aware of your personal limits is important, any athlete understands the importance of pushing themselves, however setting realistic expectations of your ability can help to prevent unnecessary injury.
Traumatic
Injuries
A traumatic injury, or trauma, is caused by something external. It may be caused by an accident such as a car accident or fall, a violent action such as a gunshot wound or beating, or it may be self-inflicted as in an attempted drug overdose. Blunt trauma, as in a car accident or fall, is the leading cause of death from traumatic injury. Diagnosis of a trauma injury may be made by physically examining the patient, by x-ray, MRI, or ultrasound scan, and by surgery if it is required.
In many cases a person suffering from a traumatic injury will receive medical advice from a paramedic or hospital doctor. A physical examination is vitally important in order to identify the severity of the injuries and identify the necessary immediate course of action to be taken. From a physical examination a doctor will be able to identify what further action is necessary. Many times x-rays and scans are performed in order to see clearly the extent of the damage. X-rays can show the presence and severity of broken bones and joint damage. Scans and MRI imaging can reveal any internal bleeding, collapsed lungs, or damage to other internal organs, including the brain. A physical examination and subsequent scanning may reveal a necessity for the patient to undergo emergency surgery. The most common reasons for trauma patients to undergo emergency surgery is to stop internal bleeding and repair extensively broken bones. Sometimes surgery is required in order to further diagnose the severity of the injuries sustained. This is referred to as diagnostic surgery.
Degenerative
Injuries
An injury may also be caused by ageing, as in arthritis and osteoporosis, or from a degenerative condition such as rheumatoid arthritis and degenerative disc disease. Arthritis and degenerative conditions affect joints over time and tend to cause pain and significant reduction in movement of the affected joints and overall mobility. With arthritic type injuries, the cartilage protecting the ends of bones wears away as we age, and also with repetitive use. As the cartilage thins and eventually wears away completely it causes bones to rub together, causing pain, inflammation, and joint stiffness. Common treatment for arthritis injuries includes gentle physical therapy to keep joints as mobile as possible, injection with steroids into the affected joint to reduce swelling and pain, or surgery. In many cases joint arthroscopies may help to remove debris from the joint that may be causing pain, and in advanced cases of arthritic injuries joint replacement may be the only treatment option. In this instance the entire degenerated joint is removed and replace with a metal or ceramic replacement. Arthritis is very common, and one in three New Zealanders over the age of 45 have arthritis.
Osteoporosis is another degenerative condition that is a common cause of injury. Osteoporosis is a disease that affects the bone density, or strength of the bones. Those with osteoporosis are at a greater risk of experiencing fracture injuries, especially hip fractures. The treatment for osteoporosis includes a variety of hormonal and other medication, as well as dietary and nutritional changes. The most common treatment for these types of degenerative injuries is surgery. Often broken bones will need to be fused back in place using pins and screws.
Injuries may occur for many reasons, whether from an outside influence such as in a car accident or from ageing or overuse such as with arthritis. Depending of the type of injury sustained, the age and health of the injured person, and the location of the injury will depend on what course of treatment is prescribed. A medical doctor who specializes in orthopaedics is qualified to deal with injuries to bones, joints, ligaments and tendons, or soft tissue of the body. Whether the injury is an athletic injury, a traumatic injury, or a degenerative based injury, an orthopaedic surgeon will offer the best treatment option for the injury sustained.
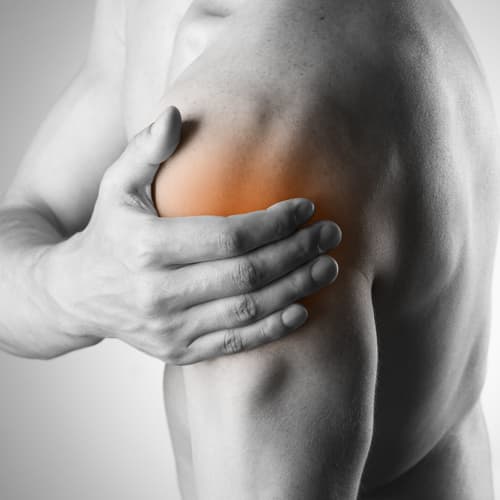
Shoulder Injuries
The shoulder is one of the most complex joints in the body, offering more range of movement than any other joint. If your shoulder is injured, day to day activities become very difficult; brushing your hair, dressing in the morning, hanging out the washing. The pain can be so debilitating that it prevents you playing sports, going fishing, getting groceries out of the trolley and sleeping. A shoulder injury can result from an accident or a pre-existing medical condition; these injuries can leave the shoulder severely weakened, in unbearable pain or completely incapacitated.
Mr Durrant is an expert in the field of shoulder injuries in both the diagnosis and treatment of the conditions and disorders that can affect the shoulder. He and his team implement the latest techniques in diagnosis, including careful physical examinations and high-field strength MRI scans, to help insure they make the correct diagnosis.
Surgery will not be necessary for all shoulder problems; Mr Durrant will assess the injury and may suggest rest and/or physical therapy. In the end, if shoulder surgery is required you can be assured of Mr Durrant’s experience and wealth of knowledge to ensure you have the best possible and least invasive treatment available.

Elbow Injuries
Your elbow is one of your more complex joints, it is essential for much of day to day life. Formed by the upper arm (the Humerus), the forearm (the Radius and Ulna), the elbow has an intricate system of ligaments and muscles, which connect the bones. Injuries to the elbow are very common and often related to degenerative conditions such as arthritis or sporting and play ground injuries, and are very painful.
Mr Durrant specialised in arthroscopic surgery, a procedure that reduces the likelihood of complications from surgery. He offers several arthroscopic elbow surgery options for elbow conditions such as tennis elbow, elbow arthritis, tricep and bicep tendon injuries, and ligament tears in throwers.
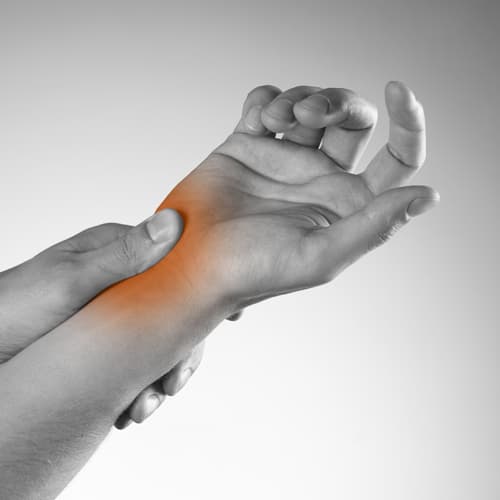
Hand and Wrist Injuries
The hand is made up of 27 bones, so with the joints, ligaments and muscles it is no surprise that hand and wrist injuries are both quite common and extremely painful. Osteoarthritis is also very common in the hand and wrist, a condition that Mr Durrant has a wealth of experience in diagnosing and treating, using both surgical and non surgical methods.
Another common complaint in the hand is carpal tunnel syndrome. Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the thumb, first and second finger, and part of the ring finger, as well as part of the palm of the hand. Mr Durrant specialises in both surgical and non surgical treatments for carpal tunnel. A carpal tunnel release procedure is one of Mr Durrants most common operations performed.
